

Now when I say “grayed” I am not talking about battle ship grey. 80% percent of you colors in representational painting will contain colors of lower intensity or chroma another words “grayed” colors. The more intense colors catch more attention when they are surrounded by colors with lower intensity. Grayed or colors of lower intensity are important way of controlling you color. Sometimes we modify all three today we are going to talk about using tertiary colors to lower or “gray down” a color’s intensity. As the artist we modify the value, intensity(chroma) or the hue. Most colors of a painting are not colors right out of the tube.

Learn more about Newton's color circle at: Munsell ColorĪrtists use a traditional color wheel based on the Red/Yellow/Blue model with secondary colors of orange, green and purple.Control your mixtures with a better understanding of the color wheel The color wheel is an invention credited to Sir Isaac Newton (1706). Nine-part harmonic triangle of Goethe begins with the printer's primaries the secondaries formed are the painter's primaries and the resulting tertiaries formed are dark neutrals.Ĭontinue tutorial, view: Complementary Colors "All colors are the friends of their neighbors and the lovers of their opposites." - Marc Chagall For Further Review The primaries are magenta, cyan, and yellow.
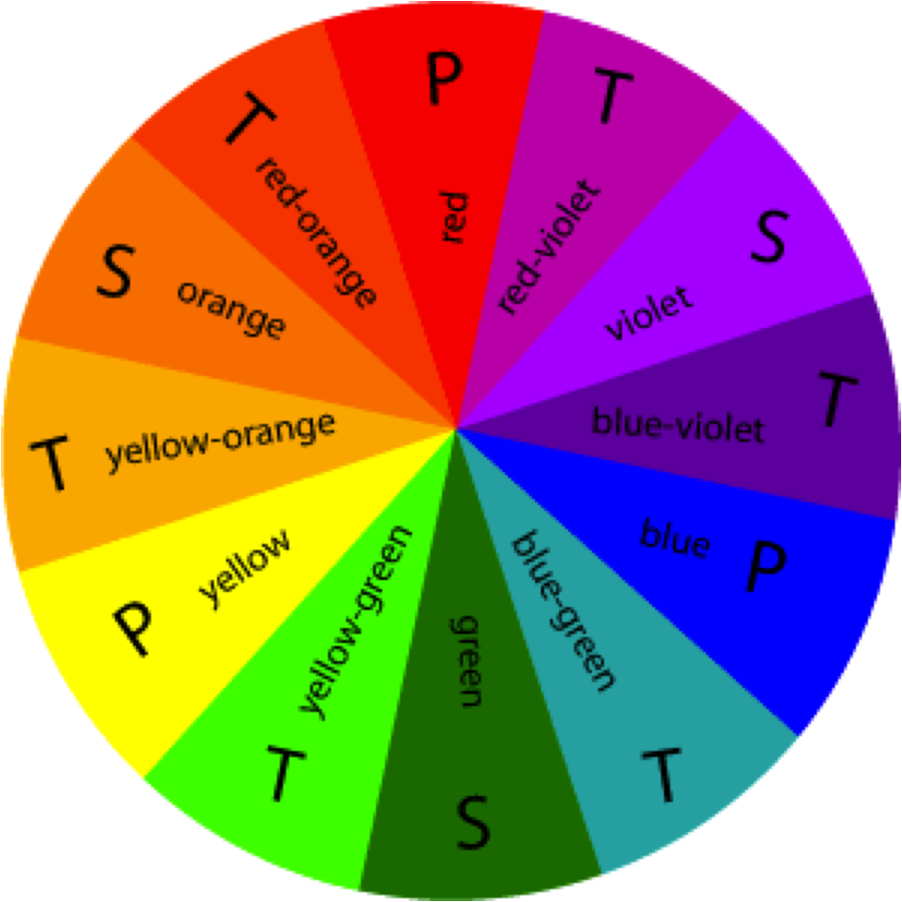
The Printers' color triangle is the set of colors used in the printing process. The primary hues are red, blue and yellow. The Painter's color triangle consists of colors we would often use in art class-those colors we learn about as children. Some colors remain visually neutral or indifferent.Ĭolor relationships may be displayed as a color wheel or a color triangle.

Tints or hues with a low saturation appear lighter than shades or highly saturated colors.Cool, low saturated, dark value hues are "passive" and visually recede.Most often warm, saturated, light value hues are "active" and visually advance.Advancing hues are most often thought to have less visual weight than the receding hues.Passive colors appear to recede when positioned against active hues. Active colors will appear to advance when placed against passive hues. The color wheel can be divided into ranges that are visually active or passive. Tertiary Colors: Those colors achieved by a mixture of primary and secondary hues.Ĭomplementary Colors: Those colors located opposite each other on a color wheel.Īnalogous Colors: Those colors located close together on a color wheel. Secondary Colors: Those colors achieved by a mixture of two primaries. Primary Colors: Colors at their basic essence those colors that cannot be created by mixing others. Begin a color wheel by positioning primary hues equidistant from one another, then create a bridge between primaries using secondary and tertiary colors. A color wheel (also referred to as a color circle) is a visual representation of colors arranged according to their chromatic relationship.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
